EKG (ECG) Interpretation
This is the EKG (ECG) for Deepak Patel from scenario SIE003US
Clinical Picture
- 64-year-old man presenting with nausea, chest tightness and shortness of breath after rushing to work.
- Extensive past medical history including cardiac issues.
- Looks tired and slightly anxious.
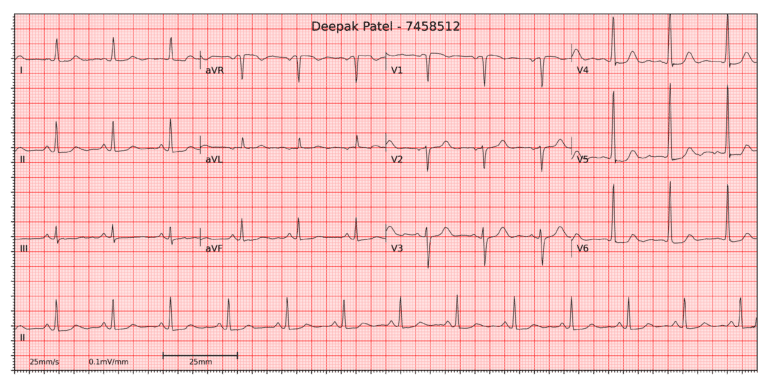
Findings
- Rate: 75
- Rhythm: Regular
- Axis: Normal
- Waves and intervals: Normal
- ST-Segment: Slight ST-depression in V4, V5 & V6 (lateral leads)
Summary
- The EKG demonstrate sinus rhythm with slight ST-depression in lateral leads.
Differential diagnosis
- In a patient with cardiac issues, presenting with nausea, chest tightness and shortness of breath after a period of exercise, slight ST-depression on an EKG is likely to indicate angina.
- In this case, when precipitated by a clear stressor such as exercise, and if the pain is transient, this is likely to be stable angina.
- Unstable angina generally has no clear precipitant and may not resolve with rest.
- A myocardial infarction is likely to show more significant EKG changes (raised ST-segment in STEMI, variable and dynamic changes in NSTEMI) and is diagnosed by the history combined with raised cardiac biomarkers such as troponin.
- A pneumothorax tends to present with sharp pain, shortness of breath and the patient may have unequal breath sounds on examination.
- Pericarditis is likely to present subacutely over a a few days
- There is no evidence of GI reflux symptoms.
Management
- In this case nitroglycerin, oxygen and reassurance are needed.
- If there is a suspicion of unstable angina or NSTEMI (for example if the pain did not resolve or there were dynamic changes on the EKG), cardiac biomarkers like Troponin should be checked as per local protocols.
Further reading
References
- Wagner, P., Strodthoff, N., Bousseljot, R., Samek, W., & Schaeffter, T. (2020). PTB-XL, a large publicly available electrocardiography dataset (version 1.0.1). PhysioNet
- Wagner, P., Strodthoff, N., Bousseljot, R.-D., Kreiseler, D., Lunze, F.I., Samek, W., Schaeffter, T. (2020), PTB-XL: A Large Publicly Available ECG Dataset. Scientific Data
- Goldberger, A. et al. (2000). PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation [Online]. 101 (23), pp. e215–e220.