EKG (ECG) Interpretation
This is the EKG (ECG) for Maria Perez from scenario SIE004US
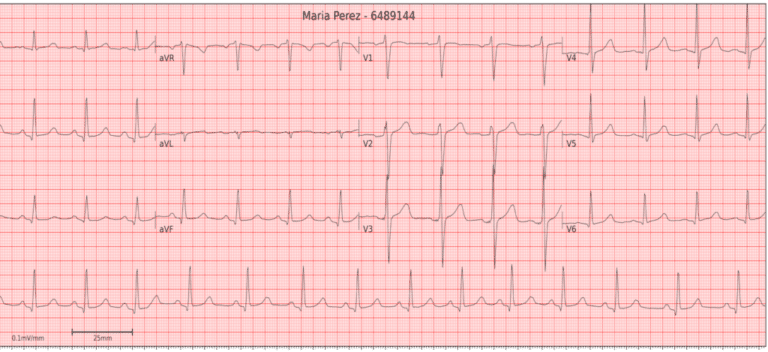
Clinical Picture
- 80-year-old woman, complaining of being lightheaded.
- Previous cardiac issues noted, with extensive past medical history.
- Looks tired and anxious.
Findings
- Rate: 55
- Rhythm: Irregular
- Axis: Normal
- Waves and intervals: Gradual increase in P-R interval
Summary
- The EKG shows second-degree heart block, type 1.
Differential diagnosis
- In a patient with cardiac issues, presenting with lightheadedness and a gradual increase in P-R interval on EKG, indicates a differential of 2nd degree heart block type 1. A myocardial infarction would show more significant EKG changes. Complete heart block would show the electrical signal can’t pass normally from the atria. Pericarditis is likely to present over a period of more than two days, and there is no evidence of GI reflux symptoms.
Management
- In this case, atropine is needed, to increase heart rate through vagolytic effects, causing an increase in cardiac output.
Further reading
References
- Wagner, P., Strodthoff, N., Bousseljot, R., Samek, W., & Schaeffter, T. (2020). PTB-XL, a large publicly available electrocardiography dataset (version 1.0.1). PhysioNet
- Wagner, P., Strodthoff, N., Bousseljot, R.-D., Kreiseler, D., Lunze, F.I., Samek, W., Schaeffter, T. (2020), PTB-XL: A Large Publicly Available ECG Dataset. Scientific Data
- Goldberger, A. et al. (2000). PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation [Online]. 101 (23), pp. e215–e220.